Deep Residual Shrinkage Network (DRSN), Deep Residual Network (ResNet) का ही एक improved version है। आसान शब्दों में कहें तो यह Deep Residual Network, Attention Mechanism और Soft Thresholding Function का एक integration है।
एक हद तक, Deep Residual Shrinkage Network के काम करने के तरीके को इस तरह समझा जा सकता है: यह Attention Mechanism के ज़रिए “unimportant features” को नोटिस करता है और Soft Thresholding Function का इस्तेमाल करके उन्हें ज़ीरो (zero) कर देता है; या दूसरे शब्दों में, यह important features को नोटिस करता है और उन्हें retain करता है (बचा कर रखता है)। इससे Deep Neural Network की noisy signals से useful features निकालने की क्षमता (ability) बढ़ जाती है।
1. Research Motivation
सबसे पहले, जब हम samples को classify करते हैं, तो samples में inevitable रूप से कुछ noise होता ही है, जैसे Gaussian Noise, Pink Noise, Laplacian Noise आदि। और broad तरीके से देखें तो, sample में ऐसी जानकारी भी हो सकती है जिसका current classification task से कोई लेना-देना नहीं है; इस जानकारी को भी noise माना जा सकता है। यह noise हमारे classification के result पर बुरा असर डाल सकता है। (Soft Thresholding कई signal denoising algorithms में एक key step है)।
Example के लिए, सड़क के किनारे बात करते समय, बातचीत की आवाज़ में गाड़ियों के हॉर्न और पहियों की आवाज़ भी mix हो सकती है। जब इन voice signals पर Speech Recognition किया जाता है, तो हॉर्न और पहियों की आवाज़ के कारण recognition result पर असर पड़ना natural है। Deep Learning के point of view से, इन हॉर्न और पहियों की आवाज़ से जुड़े features को Deep Neural Network के अंदर ही delete कर दिया जाना चाहिए, ताकि Speech Recognition पर इनका कोई impact न पड़े।
दूसरा, एक ही sample set में भी, अलग-अलग samples का noise level अक्सर अलग-अलग होता है। (यह Attention Mechanism से काफी मिलता-जुलता है; एक image sample set का example लें, तो अलग-अलग images में target object की location अलग-अलग हो सकती है; Attention Mechanism हर image के लिए target object की location को नोटिस कर सकता है)।
Example के लिए, जब हम एक Cat-Dog Classifier को train कर रहे होते हैं, तो “Dog” label वाली 5 images के लिए:
- पहली image में dog के साथ mouse हो सकता है,
- दूसरी image में dog के साथ goose हो सकता है,
- तीसरी image में dog के साथ chicken हो सकती है,
- चौथी में donkey और पांचवीं में duck हो सकती है।
जब हम classifier को train करते हैं, तो mouse, goose, chicken, donkey और duck जैसे irrelevant objects हमारे मॉडल में interference पैदा करते हैं, जिससे classification accuracy drop हो जाती है। अगर हम इन irrelevant objects को नोटिस कर सकें और उनसे जुड़े features को delete कर दें, तो Cat-Dog Classifier की accuracy improve हो सकती है।
2. Soft Thresholding
Soft Thresholding कई signal denoising algorithms का core step है। यह उन features को delete कर देता है जिनकी absolute value एक fix threshold से कम होती है, और जिनकी value इस threshold से ज्यादा होती है, उन्हें zero की direction में shrink कर देता है। इसे नीचे दिए गए formula से implement किया जा सकता है:
\[y = \begin{cases} x - \tau & x > \tau \\ 0 & -\tau \le x \le \tau \\ x + \tau & x < -\tau \end{cases}\]Soft Thresholding का output, input के respect में (derivative) इस प्रकार है:
\[\frac{\partial y}{\partial x} = \begin{cases} 1 & x > \tau \\ 0 & -\tau \le x \le \tau \\ 1 & x < -\tau \end{cases}\]जैसा कि ऊपर देखा जा सकता है, Soft Thresholding का derivative या तो 1 है या 0। यह property ReLU activation function के जैसी ही है। इसलिए, Soft Thresholding भी Deep Learning algorithms में gradient vanishing और gradient exploding के risk को कम करने में सक्षम है।
Soft Thresholding function में, threshold set करते समय दो conditions का होना ज़रूरी है: पहला, threshold एक positive number होना चाहिए; दूसरा, threshold input signal की maximum value से बड़ा नहीं होना चाहिए, वरना output पूरा zero हो जाएगा।
इसके साथ ही, threshold को तीसरी condition भी पूरी करनी चाहिए: हर sample का उसके अपने noise content के base पर अपना एक independent threshold होना चाहिए।
ऐसा इसलिए है क्योंकि कई बार samples में noise का amount अलग-अलग होता है। Example के लिए, अक्सर ऐसा होता है कि एक ही sample set में Sample A में कम noise है और Sample B में ज्यादा। ऐसे में, denoising algorithm में soft thresholding करते समय, Sample A के लिए बड़ा threshold और Sample B के लिए छोटा threshold use किया जाना चाहिए। Deep Neural Network में, भले ही इन features और thresholds का clear physical meaning न हो, लेकिन basic logic वही रहता है। यानी, हर sample का उसके noise content के हिसाब से अपना अलग threshold होना चाहिए।
3. Attention Mechanism
Computer Vision की field में Attention Mechanism को समझना काफी आसान है। जानवरों का visual system तेज़ी से पूरे area को scan कर सकता है, target object को ढूंढ सकता है, और फिर attention को उस target पर focus कर सकता है ताकि ज़्यादा details निकाली जा सकें और irrelevant information को ignore किया जा सके। Details के लिए आप Attention Mechanism पर दूसरे articles देख सकते हैं।
Squeeze-and-Excitation Network (SENet), Attention Mechanism के तहत एक नया Deep Learning method है। अलग-अलग samples में, अलग-अलग feature channels का classification task में contribution अक्सर अलग-अलग होता है। SENet एक छोटे sub-network का use करके weights का एक set हासिल करता है, और फिर इन weights को respective channels के features से multiply करता है ताकि features के size को adjust किया जा सके। इस process को अलग-अलग feature channels पर अलग-अलग level का attention लगाने के तौर पर देखा जा सकता है।
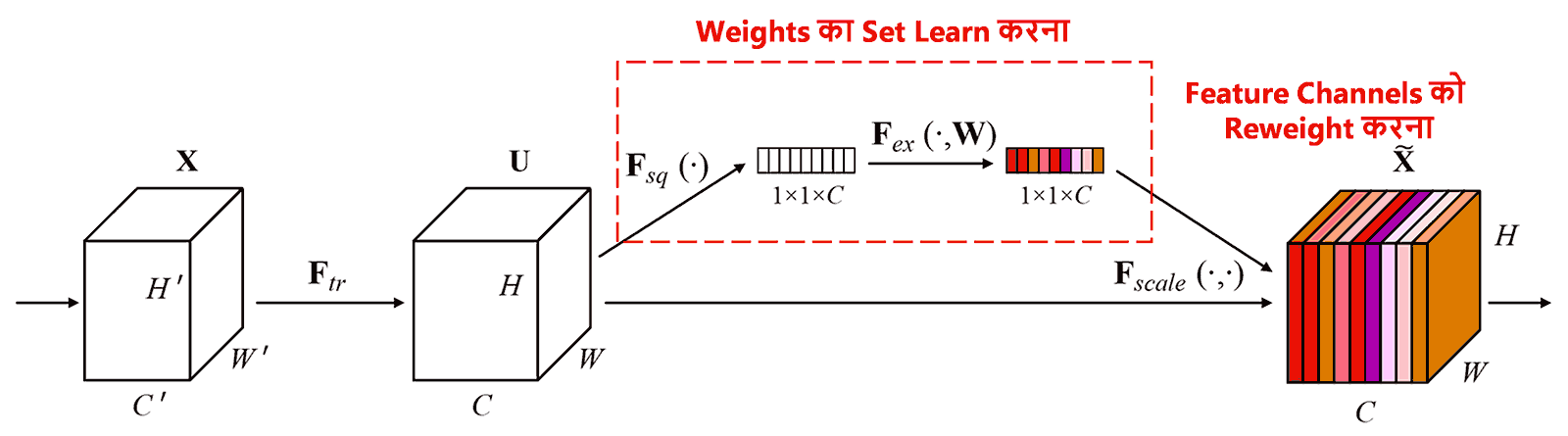
इस तरीके में, हर sample के पास weights का अपना एक independent set होगा। दूसरे शब्दों में, किन्हीं भी दो samples के weights अलग-अलग होंगे। SENet में, weights हासिल करने का path है: “Global Pooling → Fully Connected Layer → ReLU Function → Fully Connected Layer → Sigmoid Function“।
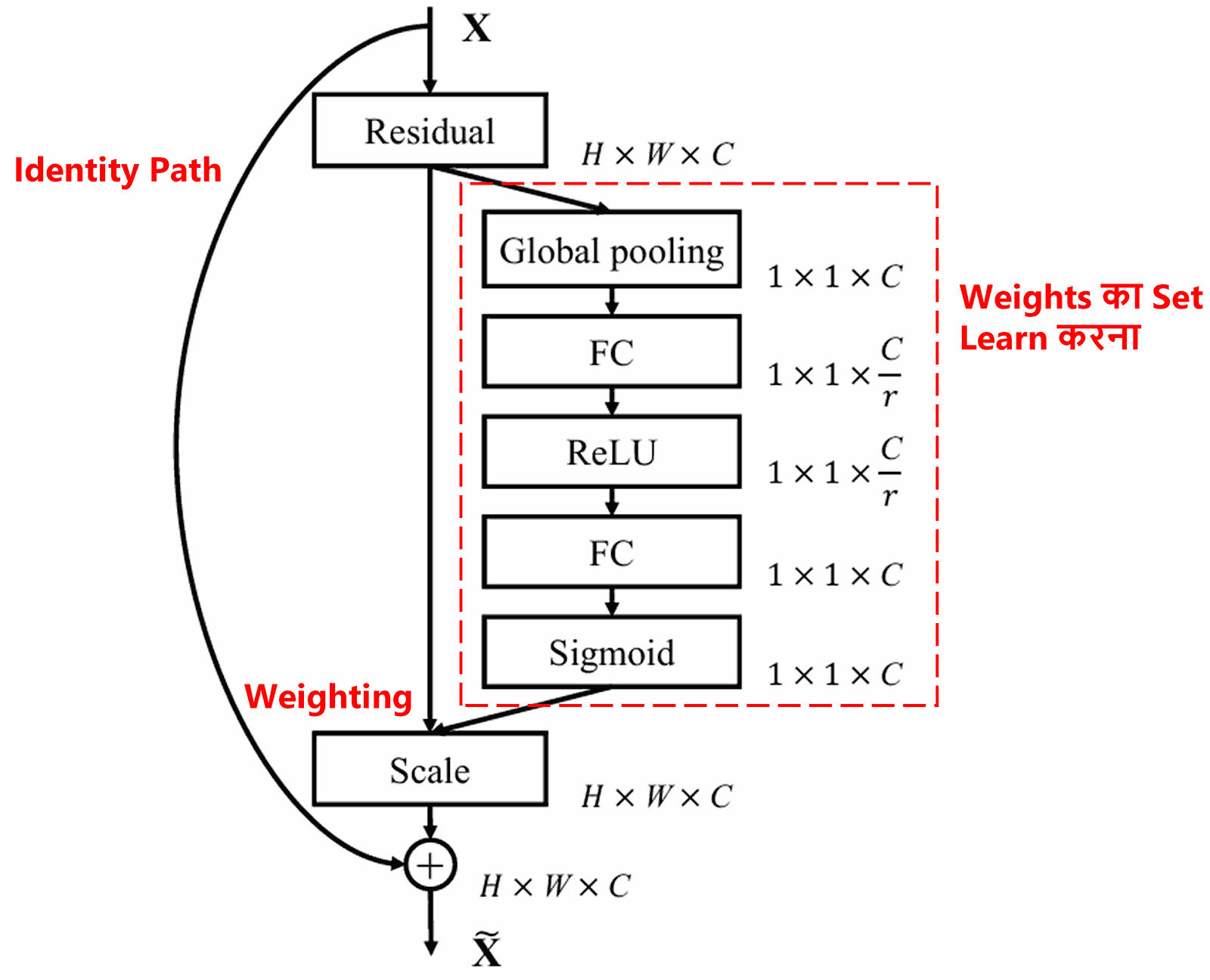
4. Deep Attention Mechanism के तहत Soft Thresholding
Deep Residual Shrinkage Network ने Deep Attention Mechanism के तहत Soft Thresholding को implement करने के लिए ऊपर बताए गए SENet के sub-network structure को adopt किया है। Red box के अंदर मौजूद sub-network के ज़रिए, यह thresholds का एक set learn कर सकता है और हर feature channel पर soft thresholding apply कर सकता है।
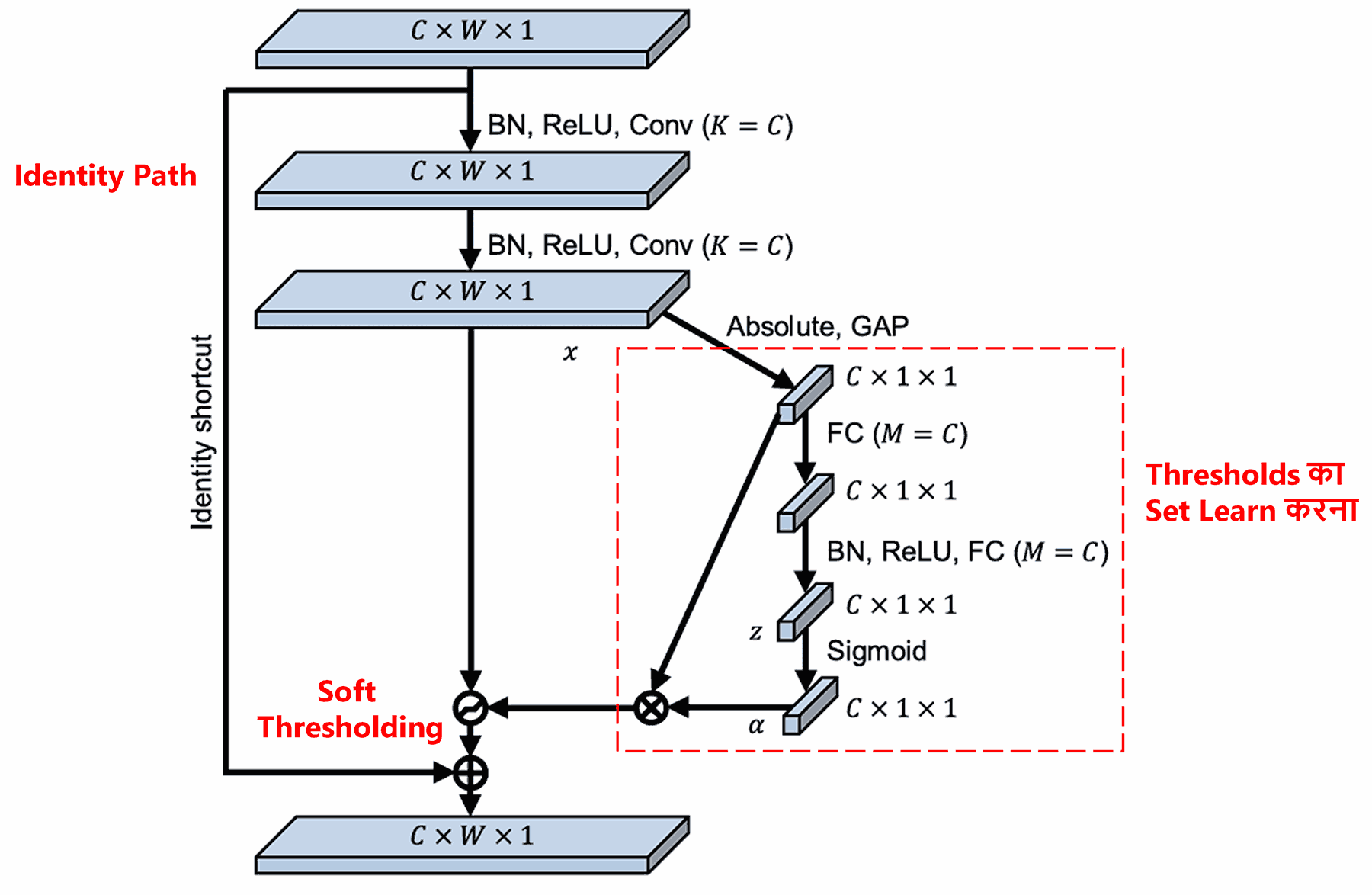
इस sub-network में, सबसे पहले input feature map के सभी features की absolute value निकाली जाती है। फिर Global Average Pooling और averaging के बाद एक feature मिलता है, जिसे ‘A’ माना जाता है। दूसरे path में, Global Average Pooling के बाद मिले feature map को एक छोटे Fully Connected Network में input किया जाता है। इस Fully Connected Network की last layer Sigmoid Function होती है, जो output को 0 और 1 के बीच normalize करती है, जिससे एक coefficient मिलता है, जिसे ‘α’ (alpha) माना जाता है।
Final threshold को α × A के रूप में show किया जा सकता है। इसलिए, threshold का मतलब है: 0 और 1 के बीच का एक number × feature map की absolute value का average। यह तरीका न केवल यह ensure करता है कि threshold positive हो, बल्कि यह भी कि वह बहुत बड़ा न हो।
इसके अलावा, अलग-अलग samples के लिए अलग-अलग thresholds होते हैं। इसलिए, एक हद तक, इसे एक special type का Attention Mechanism समझा जा सकता है: जो current task से unrelated features को नोटिस करता है, दो Convolutional Layers के ज़रिए उन्हें 0 के close ले जाता है, और Soft Thresholding के ज़रिए उन्हें पूरी तरह zero कर देता है; या फिर, जो related features को नोटिस करता है और उन्हें retain करता है (बचाए रखता है)।
Finally, कुछ basic modules के साथ Convolutional Layers, Batch Normalization, Activation Function, Global Average Pooling और Fully Connected Output Layer को stack करके पूरा Deep Residual Shrinkage Network तैयार होता है।
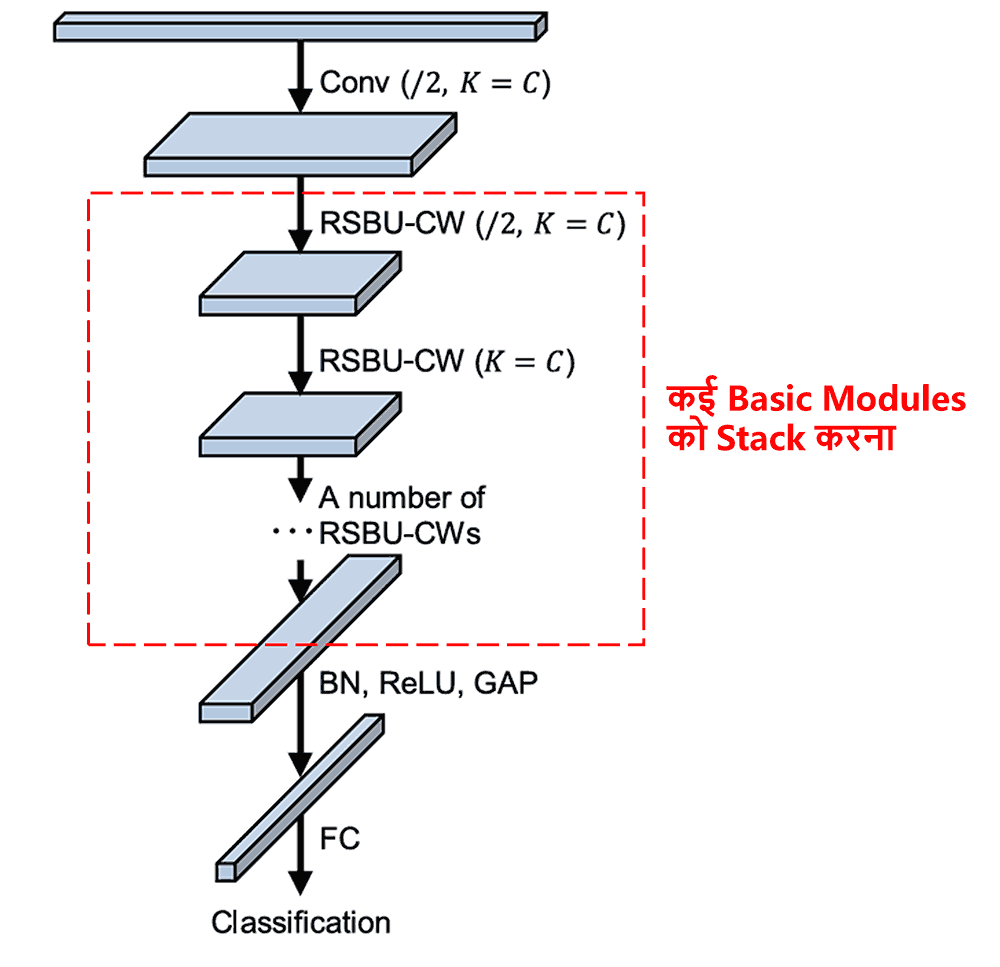
5. Generality (व्यापकता)
Deep Residual Shrinkage Network असल में एक general feature learning method है। ऐसा इसलिए है क्योंकि कई feature learning tasks में, samples में थोड़ा-बहुत noise या irrelevant information होती ही है। यह noise और irrelevant information feature learning के effect को कम कर सकती है। Example के लिए:
Image Classification के समय, अगर image में कई और objects भी हैं, तो इन objects को “noise” समझा जा सकता है; Deep Residual Shrinkage Network शायद अपने Attention Mechanism की मदद से इस “noise” को नोटिस कर सकता है और Soft Thresholding का use करके इनसे जुड़े features को zero कर सकता है, जिससे image classification की accuracy बढ़ सकती है।
Speech Recognition के समय, अगर environment noisy है (जैसे सड़क किनारे या factory में बातचीत), तो Deep Residual Shrinkage Network शायद accuracy को improve कर सकता है, या कम से कम accuracy बढ़ाने का एक idea दे सकता है।
References:
Minghang Zhao, Shisheng Zhong, Xuyun Fu, Baoping Tang, Michael Pecht, Deep residual shrinkage networks for fault diagnosis, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(7): 4681-4690.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8850096
BibTeX
@article{Zhao2020,
author = {Minghang Zhao and Shisheng Zhong and Xuyun Fu and Baoping Tang and Michael Pecht},
title = {Deep Residual Shrinkage Networks for Fault Diagnosis},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics},
year = {2020},
volume = {16},
number = {7},
pages = {4681-4690},
doi = {10.1109/TII.2019.2943898}
}
Impact
इस paper के Google Scholar पर 1400 से ज्यादा Citations हैं।
Incomplete statistics के मुताबिक, Deep Residual Shrinkage Network को 1000 से ज्यादा papers में directly apply किया गया है या improve करके mechanical, power, vision, medical, voice, text, radar, और remote sensing जैसे कई fields में use किया गया है।