Deep Residual Shrinkage Network ହେଉଛି Deep Residual Network ର ଏକ ଉନ୍ନତ ସଂସ୍କରଣ (improved variant) ଅଟେ। ମୁଖ୍ୟତଃ, ଏହା Deep Residual Network, Attention Mechanisms ଏବଂ Soft Thresholding Functions ର ଏକ ଏକୀକରଣ (integration) ଅଟେ।
କିଛି ମାତ୍ରାରେ, Deep Residual Shrinkage Network ର କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରିବାର ଶୈଳୀ (working principle) କୁ ଏହିପରି ବୁଝାଯାଇପାରେ: ଏହା attention mechanisms ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି unimportant features କୁ ଚିହ୍ନଟ କରେ ଏବଂ soft thresholding functions ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ସେଗୁଡିକୁ zero (ଶୂନ୍ୟ) କରିଦିଏ; ଅନ୍ୟ ପକ୍ଷରେ, ଏହା important features କୁ ଚିହ୍ନଟ କରି ସେଗୁଡିକୁ retain (ସଂରକ୍ଷିତ) କରେ। ଏହି ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟା noise ଥିବା signals ରୁ useful features ବାହାର କରିବାରେ deep neural network ର କ୍ଷମତାକୁ ବୃଦ୍ଧି କରିଥାଏ।
1. Research Motivation
ପ୍ରଥମତଃ, ଯେତେବେଳେ ଆମେ samples କୁ classify କରୁ, ସେତେବେଳେ noise — ଯେପରିକି Gaussian noise, pink noise, ଏବଂ Laplacian noise — ର ଉପସ୍ଥିତି ଅନିବାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଅଟେ। ବ୍ୟାପକ ଭାବରେ କହିଲେ, samples ଗୁଡିକରେ ଅନେକ ସମୟରେ ବର୍ତ୍ତମାନର classification task ସହିତ ଜଡିତ ନଥିବା information ଥାଏ, ଯାହାକୁ ମଧ୍ୟ noise ଭାବରେ ବିଚାର କରାଯାଇପାରେ। ଏହି noise classification performance ଉପରେ ଖରାପ ପ୍ରଭାବ ପକାଇପାରେ। (ଅନେକ signal denoising algorithms ରେ Soft thresholding ଏକ ମୁଖ୍ୟ ପଦକ୍ଷେପ ଅଟେ।)
ଉଦାହରଣ ସ୍ୱରୂପ, ରାସ୍ତା କଡରେ ବାର୍ତ୍ତାଳାପ ସମୟରେ, କଥାବାର୍ତ୍ତାର audio ସହିତ ଗାଡିର horns ଏବଂ ଚକର ଶବ୍ଦ ମିଶ୍ରିତ ହୋଇପାରେ। ଯେତେବେଳେ ଏହି signals ଉପରେ speech recognition କରାଯାଏ, ସେତେବେଳେ ଫଳାଫଳ ଏହି background sounds ଦ୍ୱାରା ନିଶ୍ଚିତ ଭାବରେ ପ୍ରଭାବିତ ହେବ। Deep learning ଦୃଷ୍ଟିକୋଣରୁ, horns ଏବଂ ଚକ ସହିତ ଜଡିତ features କୁ deep neural network ମଧ୍ୟରୁ eliminate (ଦୂର) କରିଦେବା ଉଚିତ୍, ଯାହାଫଳରେ ସେଗୁଡିକ speech recognition ଫଳାଫଳକୁ ପ୍ରଭାବିତ କରିବ ନାହିଁ।
ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟତଃ, ଗୋଟିଏ dataset ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା ବିଭିନ୍ନ samples ରେ noise ର ମାତ୍ରା ଭିନ୍ନ ଭିନ୍ନ ହୋଇଥାଏ। (ଏହାର attention mechanisms ସହିତ ସମାନତା ରହିଛି; ଗୋଟିଏ image dataset କୁ ଉଦାହରଣ ଭାବରେ ନେଲେ, ବିଭିନ୍ନ images ରେ target object ର location ଭିନ୍ନ ଭିନ୍ନ ହୋଇପାରେ, ଏବଂ attention mechanisms ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ image ରେ target object ର ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ location ଉପରେ ଧ୍ୟାନ କେନ୍ଦ୍ରିତ କରିପାରେ।)
ଉଦାହରଣ ସ୍ୱରୂପ, ଯେତେବେଳେ ଏକ cat-and-dog classifier କୁ train କରାଯାଏ, “dog” ଲେବଲ୍ ଥିବା ପାଞ୍ଚୋଟି images କୁ ବିଚାର କରନ୍ତୁ। ପ୍ରଥମ image ରେ କୁକୁର ସହିତ ଏକ ମୂଷା ଥାଇପାରେ, ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟରେ କୁକୁର ସହିତ ଏକ ହଂସ, ତୃତୀୟରେ କୁକୁର ସହିତ ଏକ କୁକୁଡ଼ା, ଚତୁର୍ଥରେ କୁକୁର ସହିତ ଏକ ଗଧ, ଏବଂ ପଞ୍ଚମରେ କୁକୁର ସହିତ ଏକ ବତକ ଥାଇପାରେ। Training ସମୟରେ, ମୂଷା, ହଂସ, କୁକୁଡ଼ା, ଗଧ ଏବଂ ବତକ ଭଳି irrelevant objects ଦ୍ୱାରା classifier ନିଶ୍ଚିତ ଭାବରେ ବାଧାପ୍ରାପ୍ତ ହେବ, ଯାହା ଫଳରେ classification accuracy କମିଯାଏ। ଯଦି ଆମେ ଏହି irrelevant objects — ମୂଷା, ହଂସ, କୁକୁଡ଼ା, ଗଧ ଏବଂ ବତକ — କୁ ଚିହ୍ନଟ କରିପାରିବା ଏବଂ ସେମାନଙ୍କର features କୁ eliminate କରିପାରିବା, ତେବେ cat-and-dog classifier ର accuracy ରେ ଉନ୍ନତି ଆଣିବା ସମ୍ଭବ ହେବ।
2. Soft Thresholding
Soft thresholding ହେଉଛି ଅନେକ signal denoising algorithms ର ଏକ ମୁଖ୍ୟ ପଦକ୍ଷେପ (core step)। ଏହା ସେହି features କୁ eliminate କରିଦିଏ ଯାହାର absolute values ଏକ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ threshold ଠାରୁ କମ୍ ଥାଏ ଏବଂ ଯେଉଁ features ର absolute values ଏହି threshold ଠାରୁ ଅଧିକ ଥାଏ, ସେଗୁଡିକୁ zero ଆଡକୁ shrink (ସଙ୍କୁଚିତ) କରିଦିଏ। ଏହାକୁ ନିମ୍ନଲିଖିତ formula ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି implement କରାଯାଇପାରିବ:
\[y = \begin{cases} x - \tau & x > \tau \\ 0 & -\tau \le x \le \tau \\ x + \tau & x < -\tau \end{cases}\]Input ସାପେକ୍ଷରେ soft thresholding output ର derivative ହେଉଛି:
\[\frac{\partial y}{\partial x} = \begin{cases} 1 & x > \tau \\ 0 & -\tau \le x \le \tau \\ 1 & x < -\tau \end{cases}\]ଉପରେ ଦର୍ଶାଯାଇଥିବା ପରି, soft thresholding ର derivative ହେଉଛି 1 କିମ୍ବା 0। ଏହି property ଠିକ୍ ReLU activation function ପରି। ତେଣୁ, soft thresholding ମଧ୍ୟ deep learning algorithms ରେ gradient vanishing ଏବଂ gradient exploding ର ବିପଦକୁ କମ୍ କରିପାରେ।
Soft thresholding function ରେ, threshold ର setting ଦୁଇଟି ସର୍ତ୍ତ ପୂରଣ କରିବା ଆବଶ୍ୟକ: ପ୍ରଥମତଃ, threshold ଏକ positive number ହେବା ଜରୁରୀ; ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟତଃ, threshold ଟି input signal ର maximum value ଠାରୁ ଅଧିକ ହେବା ଉଚିତ୍ ନୁହେଁ, ନଚେତ୍ output ସମ୍ପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ରୂପେ zero ହୋଇଯିବ।
ଏହା ବ୍ୟତୀତ, threshold ଟି ତୃତୀୟ ସର୍ତ୍ତ ପୂରଣ କରିବା ବାଞ୍ଛନୀୟ: ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ sample ର noise content ଉପରେ ନିର୍ଭର କରି ଏହାର ନିଜସ୍ୱ independent threshold ରହିବା ଉଚିତ୍।
ଏହାର କାରଣ ହେଉଛି samples ମଧ୍ୟରେ noise content ପ୍ରାୟତଃ ଭିନ୍ନ ହୋଇଥାଏ। ଉଦାହରଣ ସ୍ୱରୂପ, ଗୋଟିଏ dataset ରେ Sample A ରେ କମ୍ noise ଥାଇପାରେ ଯେତେବେଳେ କି Sample B ରେ ଅଧିକ noise ଥାଇପାରେ। ଏହି କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ, denoising algorithm ରେ soft thresholding କରିବା ସମୟରେ, Sample A ପାଇଁ ଏକ ଛୋଟ threshold ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯିବା ଉଚିତ୍, ଯେତେବେଳେ କି Sample B ପାଇଁ ଏକ ବଡ଼ threshold ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯିବା ଉଚିତ୍। ଯଦିଓ deep neural networks ରେ ଏହି features ଏବଂ thresholds ସେମାନଙ୍କର explicit physical definitions ହରାଇଥାନ୍ତି, ତଥାପି basic underlying logic ସମାନ ରହିଥାଏ। ଅର୍ଥାତ୍, ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ sample ର ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ noise content ଦ୍ୱାରା ନିର୍ଦ୍ଧାରିତ ନିଜସ୍ୱ independent threshold ରହିବା ଉଚିତ୍।
3. Attention Mechanism
Computer vision କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ Attention mechanisms କୁ ବୁଝିବା ଅପେକ୍ଷାକୃତ ସହଜ ଅଟେ। ପ୍ରାଣୀମାନଙ୍କର visual systems ସମଗ୍ର କ୍ଷେତ୍ରକୁ ଶୀଘ୍ର scan କରି targets କୁ ଚିହ୍ନଟ କରିପାରନ୍ତି, ଏବଂ ପରେ ଅଧିକ details ବାହାର କରିବା ପାଇଁ target object ଉପରେ attention କେନ୍ଦ୍ରିତ କରନ୍ତି ଯେତେବେଳେ କି irrelevant information କୁ suppress (ଦମନ) କରନ୍ତି। ବିସ୍ତୃତ ବିବରଣୀ ପାଇଁ, ଦୟାକରି attention mechanisms ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧୀୟ literature ଦେଖନ୍ତୁ।
Squeeze-and-Excitation Network (SENet) ହେଉଛି attention mechanisms ବ୍ୟବହାର କରୁଥିବା ଏକ ଅପେକ୍ଷାକୃତ ନୂତନ deep learning method। ବିଭିନ୍ନ samples ରେ, classification task ପାଇଁ ବିଭିନ୍ନ feature channels ର ଅବଦାନ (contribution) ପ୍ରାୟତଃ ଭିନ୍ନ ହୋଇଥାଏ। SENet ଏକ ଛୋଟ sub-network ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି weights ର ଏକ set ପାଏ ଏବଂ ତା’ପରେ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ channel ର features ର magnitude କୁ adjust କରିବା ପାଇଁ ଏହି weights କୁ ସମ୍ପୃକ୍ତ channels ର features ସହିତ multiply (ଗୁଣନ) କରେ। ଏହି ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟାକୁ ବିଭିନ୍ନ feature channels ଉପରେ ଭିନ୍ନ ଭିନ୍ନ ସ୍ତରର attention ପ୍ରୟୋଗ କରିବା ଭାବରେ ଦେଖାଯାଇପାରେ।
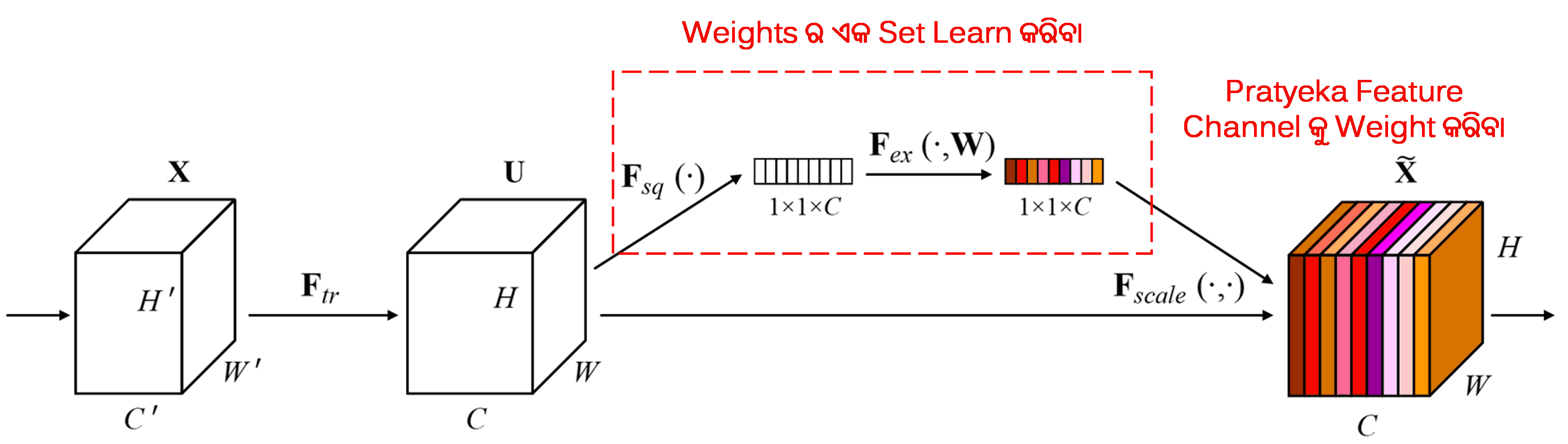
ଏହି approach ରେ, ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ sample ର ନିଜସ୍ୱ independent weights ର set ଥାଏ। ଅର୍ଥାତ୍, ଯେକୌଣସି ଦୁଇଟି samples ର weights ଭିନ୍ନ ଭିନ୍ନ ଅଟେ। SENet ରେ, weights ପାଇବାର ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ path ହେଉଛି “Global Pooling → Fully Connected Layer → ReLU Function → Fully Connected Layer → Sigmoid Function”।
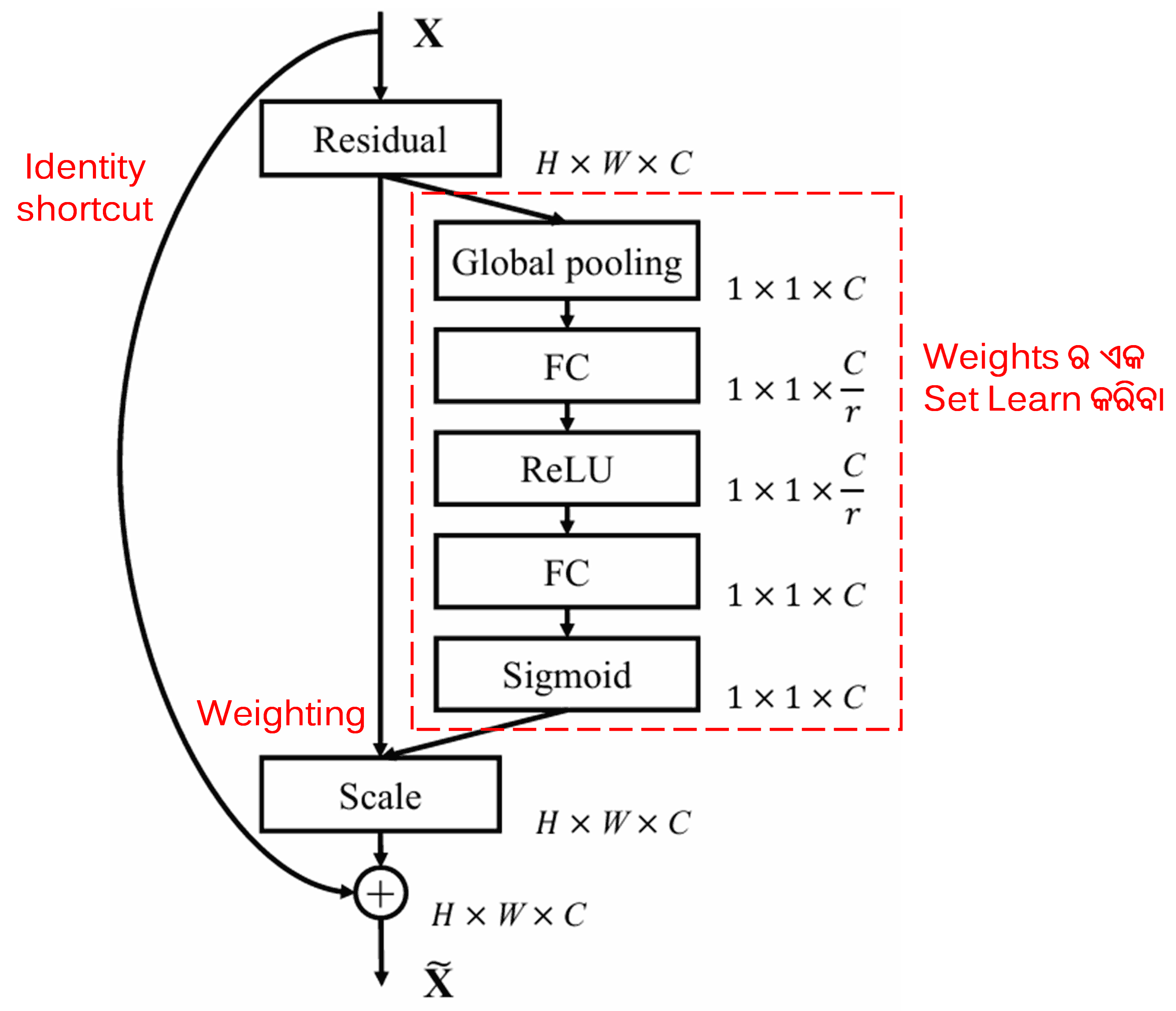
4. Soft Thresholding with Deep Attention Mechanism
Deep Attention mechanism ଅଧୀନରେ soft thresholding କୁ implement କରିବା ପାଇଁ Deep Residual Shrinkage Network ଉପରୋକ୍ତ SENet sub-network structure ରୁ ପ୍ରେରଣା ନେଇଥାଏ। Sub-network (ଯାହା ଲାଲ୍ ବାକ୍ସ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସୂଚିତ) ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ, ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ feature channel ରେ soft thresholding ପ୍ରୟୋଗ କରିବା ପାଇଁ thresholds ର ଏକ set ଶିଖାଯାଇପାରିବ (learned)।
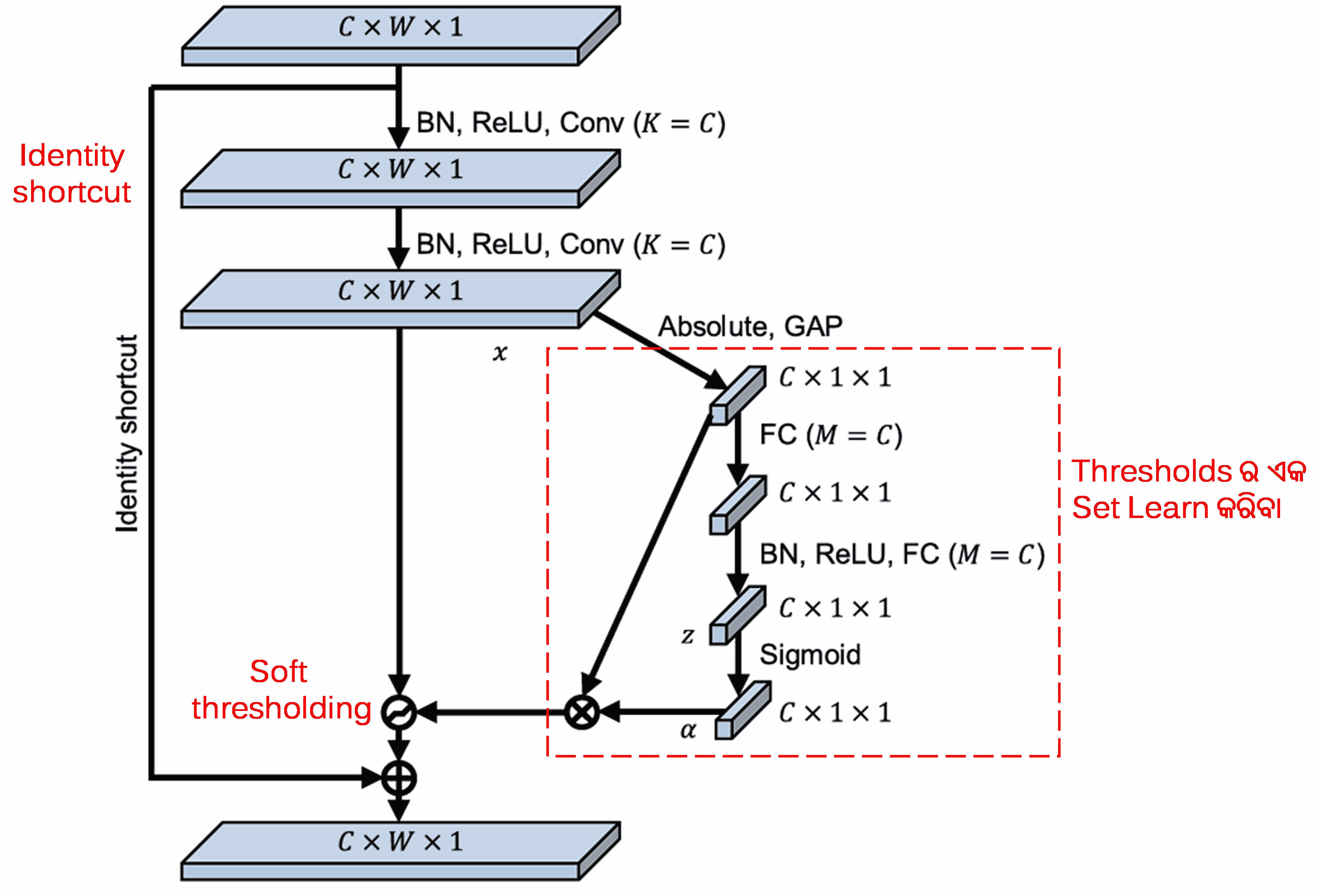
ଏହି sub-network ରେ, ପ୍ରଥମେ input feature map ର ସମସ୍ତ features ର absolute values ହିସାବ କରାଯାଏ। ତା’ପରେ, global average pooling ଏବଂ averaging ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ, ଏକ feature ମିଳେ, ଯାହାକୁ A ଭାବରେ ସୂଚିତ କରାଯାଏ। ଅନ୍ୟ path ରେ, global average pooling ପରେ ମିଳିଥିବା feature map କୁ ଏକ ଛୋଟ fully connected network ରେ input କରାଯାଏ। ଏହି fully connected network ଏହାର final layer ଭାବରେ Sigmoid function ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି output କୁ 0 ଏବଂ 1 ମଧ୍ୟରେ normalize କରେ, ଯାହା ଫଳରେ ଏକ coefficient ମିଳେ ଯାହାକୁ α ଭାବରେ ସୂଚିତ କରାଯାଏ। Final threshold କୁ α × A ଭାବରେ ପ୍ରକାଶ କରାଯାଇପାରିବ। ତେଣୁ, threshold ହେଉଛି 0 ଏବଂ 1 ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା ଏକ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ଏବଂ feature map ର absolute values ର average ର ଗୁଣନଫଳ। ଏହି method ନିଶ୍ଚିତ କରେ ଯେ threshold କେବଳ positive ନୁହେଁ ବରଂ ଅତ୍ୟଧିକ ବଡ଼ (excessively large) ମଧ୍ୟ ହେବନାହିଁ।
ଏହା ବ୍ୟତୀତ, ବିଭିନ୍ନ samples ପାଇଁ thresholds ଭିନ୍ନ ଭିନ୍ନ ହୋଇଥାଏ। ଫଳସ୍ୱରୂପ, କିଛି ମାତ୍ରାରେ, ଏହାକୁ ଏକ specialized attention mechanism ଭାବରେ ବୁଝାଯାଇପାରେ: ଏହା ବର୍ତ୍ତମାନର task ସହିତ ଜଡିତ ନଥିବା features କୁ ଚିହ୍ନଟ କରେ, ଦୁଇଟି convolutional layers ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ସେଗୁଡିକୁ zero ର ନିକଟବର୍ତ୍ତୀ values ରେ ପରିଣତ କରେ ଏବଂ soft thresholding ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି ସେଗୁଡିକୁ zero କରିଦିଏ; ଅନ୍ୟ ପକ୍ଷରେ, ଏହା ବର୍ତ୍ତମାନର task ସହିତ ଜଡିତ ଥିବା features କୁ ଚିହ୍ନଟ କରେ, ଦୁଇଟି convolutional layers ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ସେଗୁଡିକୁ zero ଠାରୁ ଦୂରରେ ଥିବା values ରେ ପରିଣତ କରେ ଏବଂ ସେଗୁଡିକୁ preserve (ସଂରକ୍ଷିତ) କରେ।
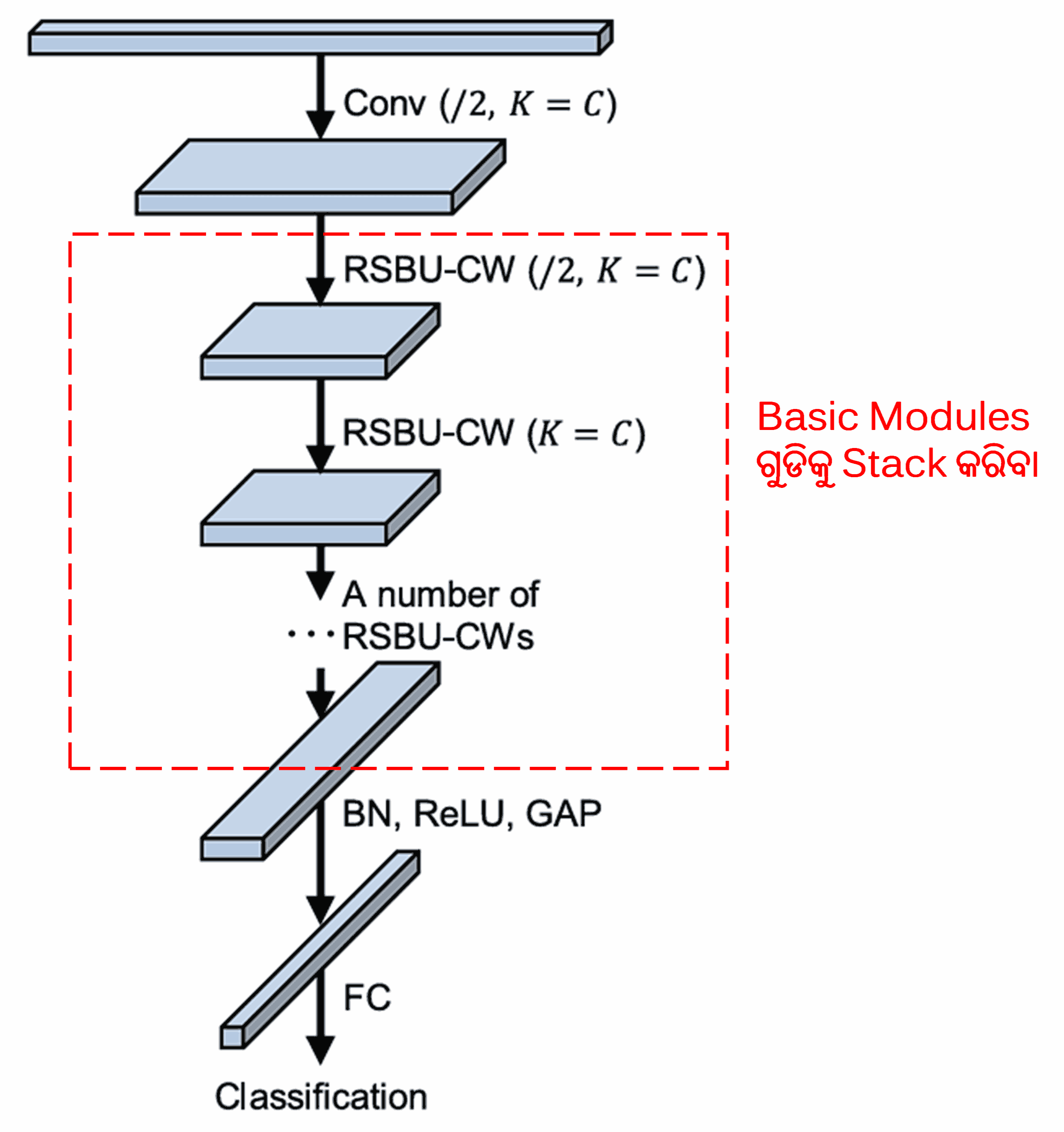
ଶେଷରେ, convolutional layers, batch normalization, activation functions, global average pooling, ଏବଂ fully connected output layers ସହିତ କିଛି ସଂଖ୍ୟକ basic modules କୁ stack କରି, ସମ୍ପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ Deep Residual Shrinkage Network ନିର୍ମାଣ କରାଯାଏ।
5. Generalization Capability
Deep Residual Shrinkage Network ବାସ୍ତବରେ ଏକ general feature learning method ଅଟେ। କାରଣ ହେଉଛି, ଅନେକ feature learning tasks ରେ, samples ରେ କମ୍ କିମ୍ବା ବେଶୀ କିଛି noise ଏବଂ irrelevant information ରହିଥାଏ। ଏହି noise ଏବଂ irrelevant information feature learning ର performance କୁ ପ୍ରଭାବିତ କରିପାରେ। ଉଦାହରଣ ସ୍ୱରୂପ:
Image classification ରେ, ଯଦି ଏକ image ରେ ଏକାସାଙ୍ଗରେ ଅନ୍ୟ ଅନେକ objects ଥାଏ, ତେବେ ଏହି objects କୁ “noise” ଭାବରେ ବୁଝାଯାଇପାରେ। Deep Residual Shrinkage Network ହୁଏତ attention mechanism ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି ଏହି “noise” କୁ ଲକ୍ଷ୍ୟ କରିପାରେ ଏବଂ ତା’ପରେ soft thresholding ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି ଏହି “noise” ସହିତ ଜଡିତ features କୁ zero କରିପାରେ, ଯାହା ଦ୍ୱାରା image classification accuracy ରେ ଉନ୍ନତି ହୋଇପାରେ।
Speech recognition ରେ, ବିଶେଷ ଭାବରେ ରାସ୍ତା କଡରେ କିମ୍ବା factory workshop ଭିତରେ କଥାବାର୍ତ୍ତା ଭଳି ଅପେକ୍ଷାକୃତ noisy environments ରେ, Deep Residual Shrinkage Network speech recognition accuracy କୁ improve କରିପାରେ, କିମ୍ବା ଅନ୍ତତଃ ପକ୍ଷେ, ଏକ methodology ପ୍ରଦାନ କରେ ଯାହା speech recognition accuracy କୁ improve କରିବାରେ ସକ୍ଷମ ହୋଇପାରେ।
Reference
Minghang Zhao, Shisheng Zhong, Xuyun Fu, Baoping Tang, Michael Pecht, Deep residual shrinkage networks for fault diagnosis, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(7): 4681-4690.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8850096
BibTeX
@article{Zhao2020,
author = {Minghang Zhao and Shisheng Zhong and Xuyun Fu and Baoping Tang and Michael Pecht},
title = {Deep Residual Shrinkage Networks for Fault Diagnosis},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics},
year = {2020},
volume = {16},
number = {7},
pages = {4681-4690},
doi = {10.1109/TII.2019.2943898}
}
Academic Impact
ଏହି paper କୁ Google Scholar ରେ 1,400 ରୁ ଅଧିକ citations ମିଳିଛି।
ଅସମ୍ପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ପରିସଂଖ୍ୟାନ (incomplete statistics) ଅନୁଯାୟୀ, Deep Residual Shrinkage Network (DRSN) କୁ mechanical engineering, electrical power, vision, healthcare, speech, text, radar, ଏବଂ remote sensing ସହିତ ବିଭିନ୍ନ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ 1,000 ରୁ ଅଧିକ publications/studies ରେ ସିଧାସଳଖ apply କରାଯାଇଛି କିମ୍ବା modify କରି apply କରାଯାଇଛି।