Di Deep Residual Shrinkage Network na wan improved version of di Deep Residual Network. Basically, di Deep Residual Shrinkage Network don join Deep Residual Network, attention mechanisms, en soft thresholding functions togeda inside wan system.
Mek we try ondastand how di Deep Residual Shrinkage Network de wok. Fuss, di network de yuz attention mechanisms fo identify den unimportant features. Den, di network de yuz soft thresholding functions fo turn den unimportant features to zero. On di oda hand, di network de identify di important features en e de kip dem. Dis process de mek di deep neural network get more pawa. E de help di network extract useful features from signals wey get noise inside.
1. Research Motivation
Fuss, noise na sometin wey we nor go fit avoid wey di algorithm de classify samples. Examples of dis noise na Gaussian noise, pink noise, en Laplacian noise. If we look am broad wan, samples kin get information wey nor get anytin fo du wit di classification task wey we de du. We kin tek dis irrelevant information as noise. Dis noise kin mek di classification performance go down. (Soft thresholding na wan key step inside plenty signal denoising algorithms.)
Mek we tek wan example. Imagine person de tok by di roadside. Di audio go get sound from motocar horn en wheel. If we want du speech recognition on top den signals, di background sound go definitely affect di result. From deep learning perspective, di deep neural network suppose to commot di features wey represent di horn en di wheel. If e commot am, den features nor go disturb di speech recognition results.
Number two, di amount of noise kin different from sample to sample. Dis kain change de happen even inside di sem dataset. (Dis change favor wetin we de call attention mechanisms. Mek we tek image dataset as example. Di location of di target object kin different inside different picture. Attention mechanisms fit focus on di specific location of di target object inside each image.)
Fo example, mek we se we de train wan cat-and-dog classifier wit five images wey get label “dog.” Image 1 fit get dog en mouse. Image 2 fit get dog en goose. Image 3 fit get dog en chicken. Image 4 fit get dog en donkey. Image 5 fit get dog en duck. Wey di training de go on, den irrelevant objects lek mouse, goose, chicken, donkey, en duck go disturb di classifier. Dis disturbance go mek di classification accuracy go down. But if we fit identify den irrelevant objects, den we go fit commot di features wey correspond to den objects. Na so we go fit improve di accuracy of di cat-and-dog classifier.
2. Soft Thresholding
Soft thresholding na wan core step inside plenty signal denoising algorithms. Di algorithm de commot features if di absolute values of di features small pass wan particular threshold. But if di absolute values of di features big pass dis threshold, di algorithm go shrink di features go towards zero. Researchers kin yuz dis formula fo du soft thresholding:
\[y = \begin{cases} x - \tau & x > \tau \\ 0 & -\tau \le x \le \tau \\ x + \tau & x < -\tau \end{cases}\]Di derivative of di soft thresholding output wit respect to di input na:
\[\frac{\partial y}{\partial x} = \begin{cases} 1 & x > \tau \\ 0 & -\tau \le x \le \tau \\ 1 & x < -\tau \end{cases}\]Di formula wey de up de sho se di derivative of soft thresholding na either 1 or 0. Dis property sem sem lek di property of ReLU activation function. So, soft thresholding fit reduce di risk of gradient vanishing en gradient exploding inside deep learning algorithms.
Inside di soft thresholding function, di way we set di threshold must follow two conditions. Fuss, di threshold must bi positive number. Second, di threshold nor suppose big pass di maximum value of di input signal. If not, all di output go just turn to zero.
Also, e go beta if di threshold follow wan third condition. Each sample suppose get e own independent threshold based on di amount of noise wey de inside da sample.
Di rizin na dat noise content kin different among samples. Fo example, inside di sem dataset, Sample A fit get small noise while Sample B get plenty noise. Inside dis case, Sample A suppose yuz small threshold during soft thresholding. Sample B suppose yuz big threshold. Even though den features en thresholds nor get clear physical definitions inside deep neural networks, di basic logic na di sem. In oda words, each sample suppose get independent threshold. Na di specific noise content de determine dis threshold.
3. Attention Mechanism
Researchers fit ondastand attention mechanisms easy wan inside di field of computer vision. Di visual system of animal dem fit distinguish targets wey dem scan di area fast fast. Den, di visual system go focus attention on di target object. Dis action de mek di system extract more details. Sem time, di system de suppress irrelevant information. If una wan sabi more, una fit check literature bout attention mechanisms.
Di Squeeze-and-Excitation Network (SENet) represent wan deep learning method wey new small en e de yuz attention mechanisms. Across different samples, different feature channels de contribute different way to di classification task. SENet de yuz wan small sub-network fo get wan set of weights. Den, SENet de multiply den weights by di features of di respective channels. Dis operation de adjust di magnitude of di features inside each channel. We fit si dis process as applying different levels of attention to different feature channels.
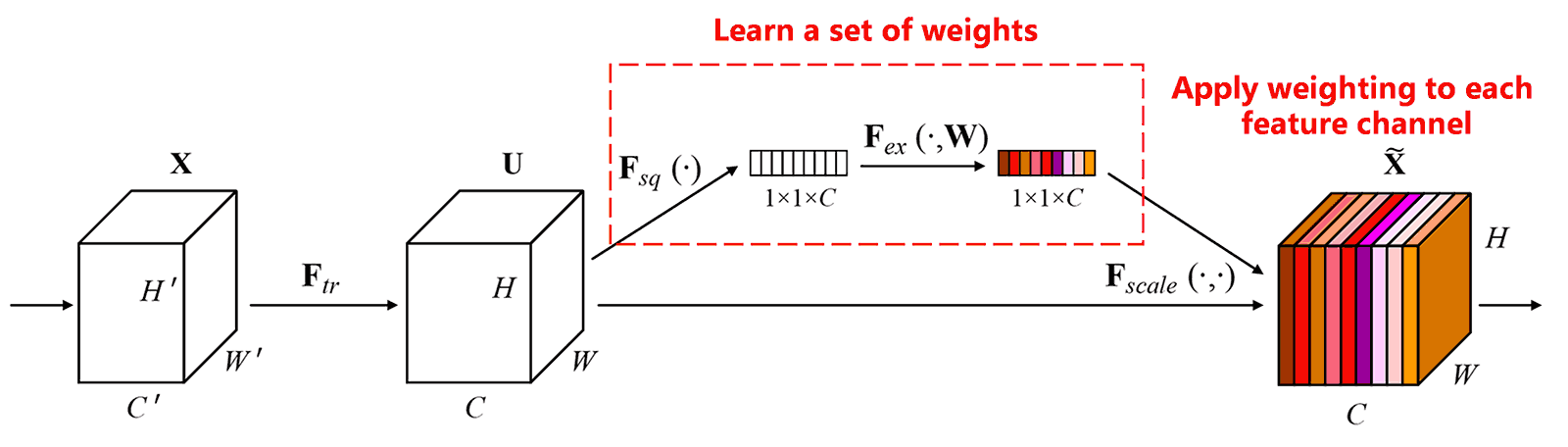
Inside dis approach, every sample get e own independent set of weights. Dat min se, di weights fo any two arbitrary samples are different. Inside SENet, di specific path fo get weights na “Global Pooling → Fully Connected Layer → ReLU Function → Fully Connected Layer → Sigmoid Function.”
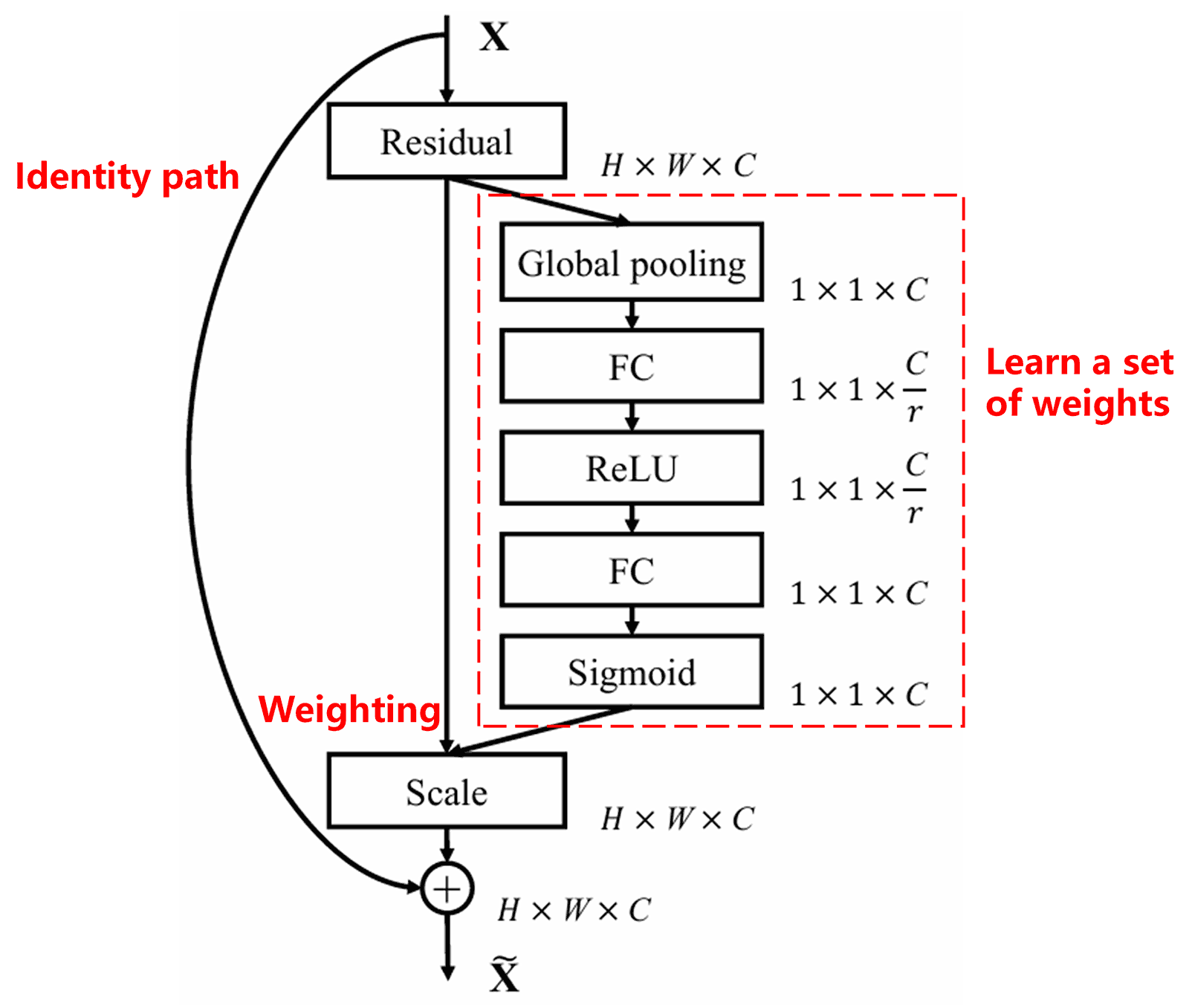
4. Soft Thresholding with Deep Attention Mechanism
Di Deep Residual Shrinkage Network de yuz di structure of di SENet sub-network. Di network de yuz dis structure fo implement soft thresholding under deep attention mechanism. Di sub-network (wey de inside di red box) de Learn a set of thresholds. Den, di network de apply soft thresholding to each feature channel yuzing den thresholds.
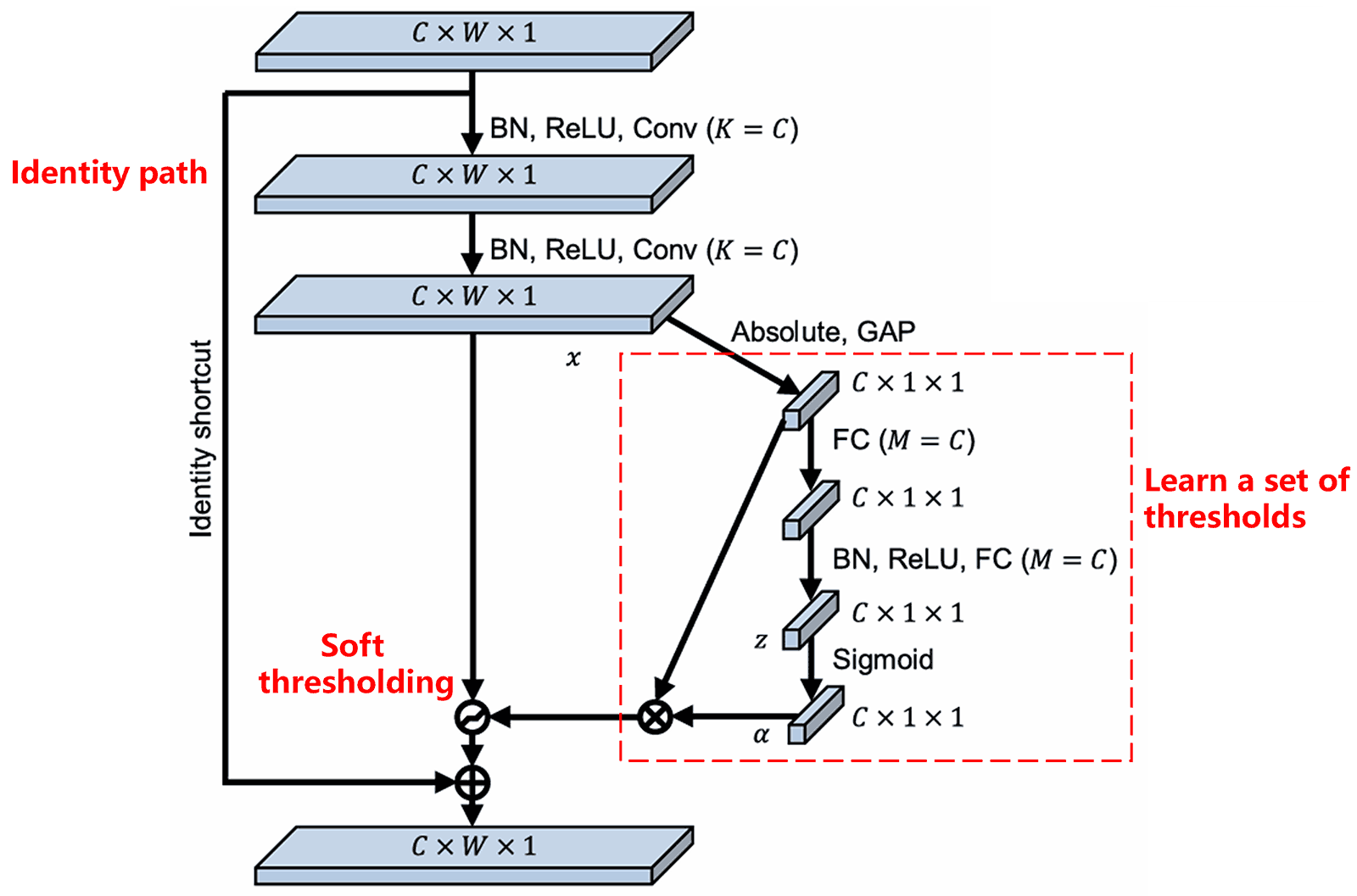
Inside dis sub-network, di system go fuss calculate di absolute values of all features inside di input feature map. Den, di system de du global average pooling en averaging fo get wan feature, wey we call A. Inside di oda path, di system de input di feature map into wan small fully connected network after global average pooling. Dis fully connected network de yuz Sigmoid function as di final layer. Dis function de normalize di output between 0 en 1. Dis process de giv we wan coefficient, wey we call α. We fit express di final threshold as α × A. So, di threshold na di product of two numbers. Wan number de between 0 en 1. Di oda number na di average of di absolute values of di feature map. Dis method de mek sure se di threshold na positive. Dis method de also mek sure se di threshold nor too big.
Furthermore, different samples de result in different thresholds. As a result, we fit ondastand dis method as wan specialized attention mechanism. Di mechanism de identify features wey nor relevant to di current task. Di mechanism de transform den features into values wey close to zero via two convolutional layers. Den, di mechanism de set den features to zero yuzing soft thresholding. Or we fit se, di mechanism de identify features wey relevant to di current task. Di mechanism de transform den features into values wey far from zero via two convolutional layers. Finally, di mechanism de preserve den features.
Finally, we go Stack many basic modules. We also put convolutional layers, batch normalization, activation functions, global average pooling, en fully connected output layers. Na dis process de construct di complete Deep Residual Shrinkage Network.
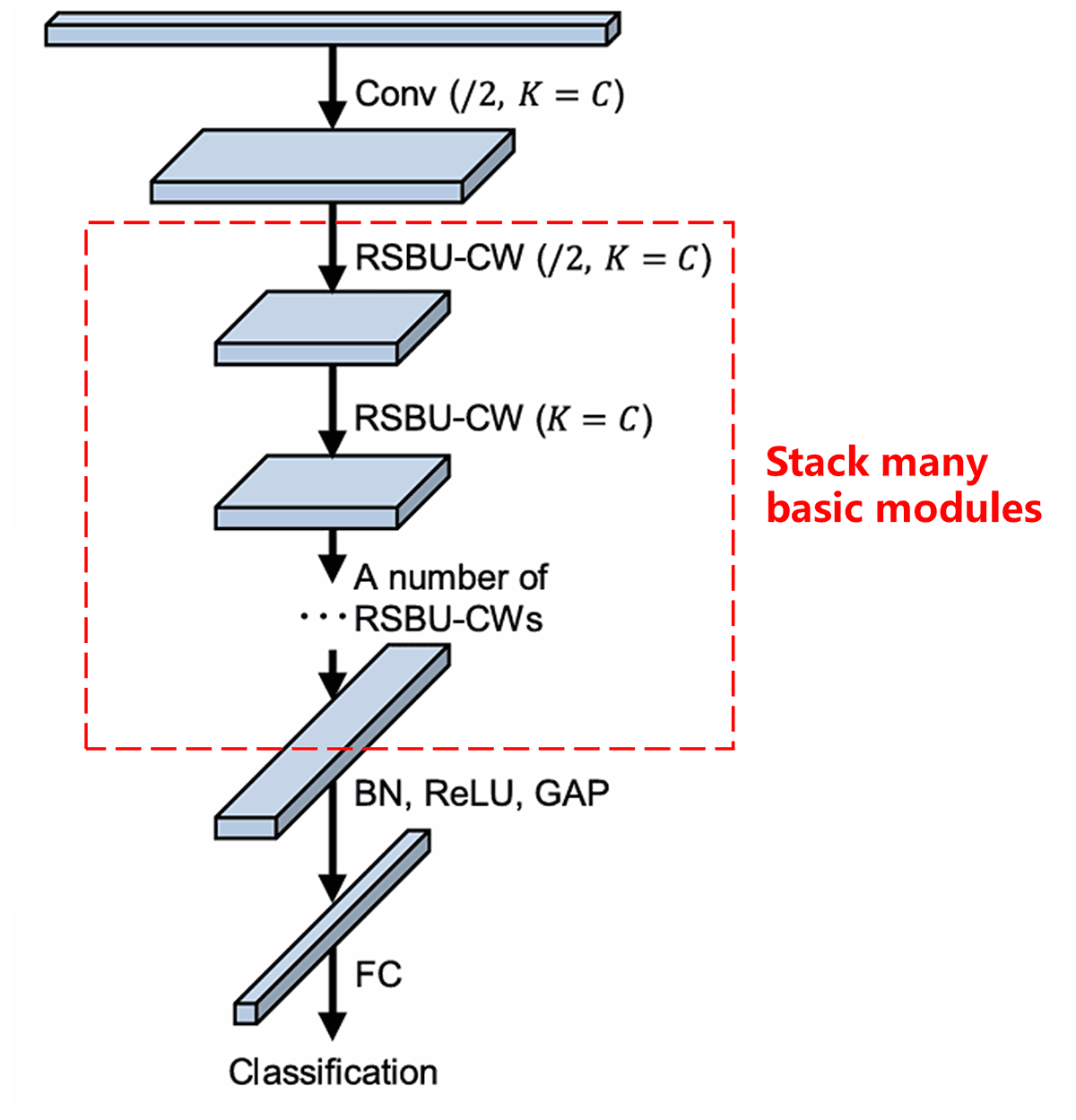
5. Generalization Capability
Di Deep Residual Shrinkage Network na wan general method fo feature learning. Di rizin na dat samples often get noise inside plenty feature learning tasks. Samples also get irrelevant information. Dis noise en irrelevant information fit affect di performance of feature learning. Lek we se:
Mek we consider image classification. Wan picture fit get plenty oda objects inside am sem time. We fit ondastand den objects as “noise.” Di Deep Residual Shrinkage Network fit able to yuz di attention mechanism. Di network go notis dis “noise.” Den, di network go employ soft thresholding fo set di features corresponding to dis “noise” to zero. Dis action fit improve image classification accuracy.
Mek we consider speech recognition. Specifically, consider environments wey get plenty noise lek conversational settings by roadside or inside factory workshop. Di Deep Residual Shrinkage Network fit improve speech recognition accuracy. Or at least, di network offer wan methodology. Dis methodology fit improve speech recognition accuracy.
6. Academic Impact
Dis paper don get ova 1,400 citations on Google Scholar.
Based on statistics wey neva complete, researchers don apply di Deep Residual Shrinkage Network (DRSN) inside ova 1,000 publications/studies. Den applications cover plenty fields. Den fields include mechanical engineering, electrical power, vision, healthcare, speech, text, radar, en remote sensing.
Reference
Minghang Zhao, Shisheng Zhong, Xuyun Fu, Baoping Tang, Michael Pecht, Deep residual shrinkage networks for fault diagnosis, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(7): 4681-4690.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8850096
BibTeX
@article{Zhao2020,
author = {Minghang Zhao and Shisheng Zhong and Xuyun Fu and Baoping Tang and Michael Pecht},
title = {Deep Residual Shrinkage Networks for Fault Diagnosis},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics},
year = {2020},
volume = {16},
number = {7},
pages = {4681-4690},
doi = {10.1109/TII.2019.2943898}
}