Deep Residual Shrinkage Network، درحقیقت Deep Residual Network کا ایک improved variant ہے۔ اصل میں، یہ Deep Residual Network، attention mechanisms، اور soft thresholding functions کا integration ہے۔
ایک حد تک، Deep Residual Shrinkage Network کا working principle اس طرح سمجھا جا سکتا ہے: یہ attention mechanisms کا استعمال کرتے ہوئے unimportant features کو identify کرتا ہے اور soft thresholding functions کے ذریعے انہیں zero سیٹ کر دیتا ہے؛ اس کے برعکس، یہ important features کو identify کرتا ہے اور انہیں retain کرتا ہے۔ یہ process، deep neural network کی noise والے signals سے useful features extract کرنے کی صلاحیت کو بڑھاتا ہے۔
1. Research Motivation
پہلے، جب samples کو classify کیا جاتا ہے، تو noise کی موجودگی—جیسے کہ Gaussian noise، pink noise، اور Laplacian noise—ناگزیر (inevitable) ہے۔ وسیع پیمانے پر، samples میں اکثر ایسی معلومات ہوتی ہے جو current classification task سے irrelevant ہوتی ہے، جسے noise بھی سمجھا جا سکتا ہے۔ یہ noise classification performance پر منفی اثر ڈال سکتی ہے۔ (Soft thresholding بہت سے signal denoising algorithms میں ایک key step ہے۔)
مثال کے طور پر، سڑک کے کنارے گفتگو کے دوران، audio میں گاڑی کے horns اور wheels کی آوازیں شامل ہو سکتی ہیں۔ جب ان signals پر speech recognition perform کیا جاتا ہے، تو results لازمی طور پر ان background sounds سے متاثر ہوں گے۔ Deep learning کے نقطہ نظر سے، horns اور wheels سے متعلقہ features کو deep neural network کے اندر eliminate کر دینا چاہیے تاکہ وہ speech recognition results کو effect نہ کریں۔
دوسرا، ایک ہی dataset کے اندر بھی، noise کی مقدار اکثر sample to sample vary کرتی ہے۔ (اس میں attention mechanisms کے ساتھ مماثلت ہے؛ ایک image dataset کی مثال لیں، تو target object کی location مختلف images میں مختلف ہو سکتی ہے، اور attention mechanisms ہر image میں target object کی specific location پر focus کر سکتے ہیں۔)
مثال کے طور پر، cat-and-dog classifier کو train کرتے وقت، فرض کریں “dog” لیبل والی 5 images ہیں۔ پہلی image میں dog اور mouse ہو سکتے ہیں، دوسری میں dog اور goose، تیسری میں dog اور chicken، چوتھی میں dog اور donkey، اور پانچویں میں dog اور duck۔ Training کے دوران، classifier لازمی طور پر irrelevant objects جیسے کہ mice، geese، chickens، donkeys، اور ducks سے interfere ہوگا، جس سے classification accuracy کم ہو سکتی ہے۔ اگر ہم ان irrelevant objects—یعنی mice، geese، chickens، donkeys، اور ducks—کو identify کر سکیں اور ان کے corresponding features کو eliminate کر دیں، تو cat-and-dog classifier کی accuracy کو improve کرنا ممکن ہے۔
2. Soft Thresholding
Soft thresholding بہت سے signal denoising algorithms میں ایک core step ہے۔ یہ ان features کو eliminate کرتا ہے جن کی absolute values ایک خاص threshold سے کم ہوتی ہیں اور ان features کو zero کی طرف shrink کرتا ہے جن کی absolute values اس threshold سے زیادہ ہوتی ہیں۔ اسے درج ذیل formula کے ذریعے implement کیا جا سکتا ہے:
\[y = \begin{cases} x - \tau & x > \tau \\ 0 & -\tau \le x \le \tau \\ x + \tau & x < -\tau \end{cases}\]Soft thresholding output کا input کے لحاظ سے derivative یہ ہے:
\[\frac{\partial y}{\partial x} = \begin{cases} 1 & x > \tau \\ 0 & -\tau \le x \le \tau \\ 1 & x < -\tau \end{cases}\]جیسا کہ اوپر دکھایا گیا ہے، soft thresholding کا derivative یا تو 1 ہے یا 0۔ یہ property بالکل ReLU activation function جیسی ہی ہے۔ اس لیے، soft thresholding، deep learning algorithms کو gradient vanishing اور gradient exploding کے risk سے بچانے میں بھی مدد کر سکتا ہے۔
Soft thresholding function میں، threshold کی setting کو دو شرطوں (conditions) کو پورا کرنا چاہیے: پہلا، threshold ایک positive number ہونا چاہیے؛ دوسرا، threshold، input signal کی maximum value سے زیادہ نہیں ہونا چاہیے، ورنہ output پورا zero ہو جائے گا۔
مزید برآں، threshold کے لیے تیسری شرط کو پورا کرنا بہتر ہے: ہر sample کا اس کے noise content کی بنیاد پر اپنا independent threshold ہونا چاہیے۔
اس کی وجہ یہ ہے کہ samples کے درمیان noise content اکثر vary کرتا ہے۔ مثال کے طور پر، اکثر ایسا ہوتا ہے کہ ایک ہی dataset میں Sample A میں noise کم ہو جبکہ Sample B میں noise زیادہ ہو۔ اس صورت میں، denoising algorithm میں soft thresholding perform کرتے وقت، Sample A کے لیے چھوٹا threshold استعمال ہونا چاہیے، جبکہ Sample B کے لیے بڑا threshold استعمال ہونا چاہیے۔ اگرچہ deep neural networks میں ان features اور thresholds کی explicit physical definitions ختم ہو جاتی ہیں، لیکن بنیادی logic وہی رہتی ہے۔ دوسرے لفظوں میں، ہر sample کا اپنا independent threshold ہونا چاہیے جو اس کے specific noise content سے determine کیا گیا ہو۔
3. Attention Mechanism
Computer Vision کی field میں Attention mechanisms کو سمجھنا نسبتاً آسان ہے۔ جانوروں کا visual system پورے area کو تیزی سے scan کر کے targets کو distinguish کر سکتا ہے، اور بعد میں attention کو target object پر focus کر کے مزید details extract کرتا ہے جبکہ irrelevant information کو suppress کرتا ہے۔ تفصیلات کے لیے، براہ کرم attention mechanisms سے متعلقہ literature دیکھیں۔
Squeeze-and-Excitation Network (SENet) ایک نسبتاً نیا deep learning method ہے جو attention mechanisms کا استعمال کرتا ہے۔ مختلف samples میں، classification task میں مختلف feature channels کا contribution اکثر مختلف ہوتا ہے۔ SENet ایک چھوٹا sub-network استعمال کرتا ہے تاکہ Learn a set of weights (weights کا ایک set حاصل کیا جا سکے) اور پھر ان weights کو respective channels کے features سے multiply کرتا ہے تاکہ ہر channel میں features کے magnitude کو adjust کیا جا سکے۔ اس process کو مختلف feature channels پر مختلف levels کی attention apply کرنے کے طور پر دیکھا جا سکتا ہے (Apply weighting to each feature channel)۔
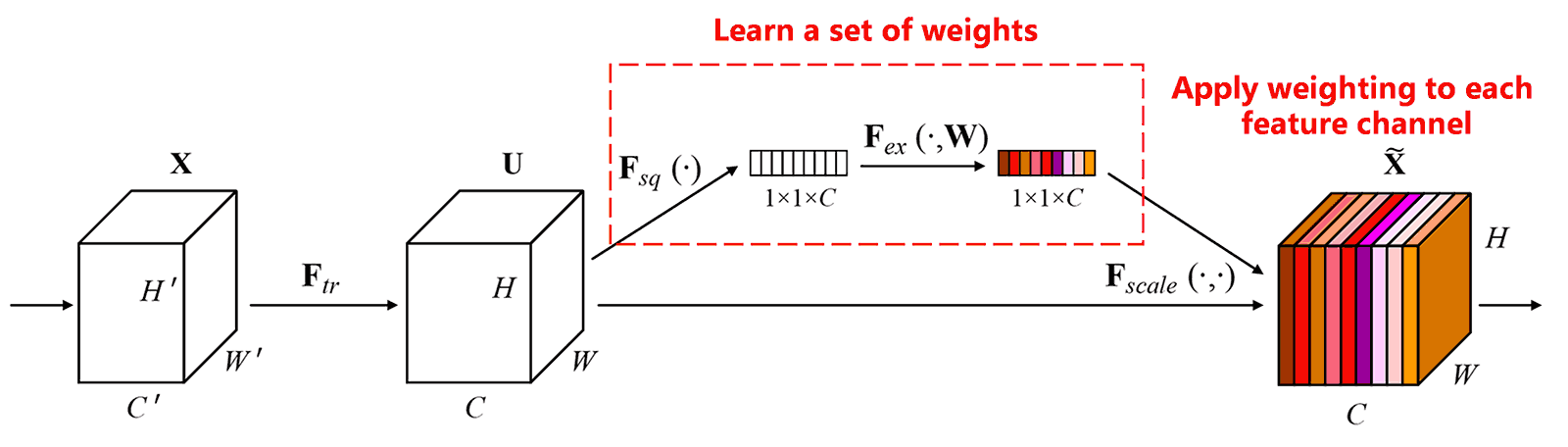
اس approach میں، ہر sample کا weights کا اپنا independent set ہوتا ہے۔ دوسرے لفظوں میں، کسی بھی دو arbitrary samples کے weights مختلف ہوتے ہیں۔ SENet میں، weights حاصل کرنے کا specific path یہ ہے: “Global Pooling → Fully Connected Layer → ReLU Function → Fully Connected Layer → Sigmoid Function”۔
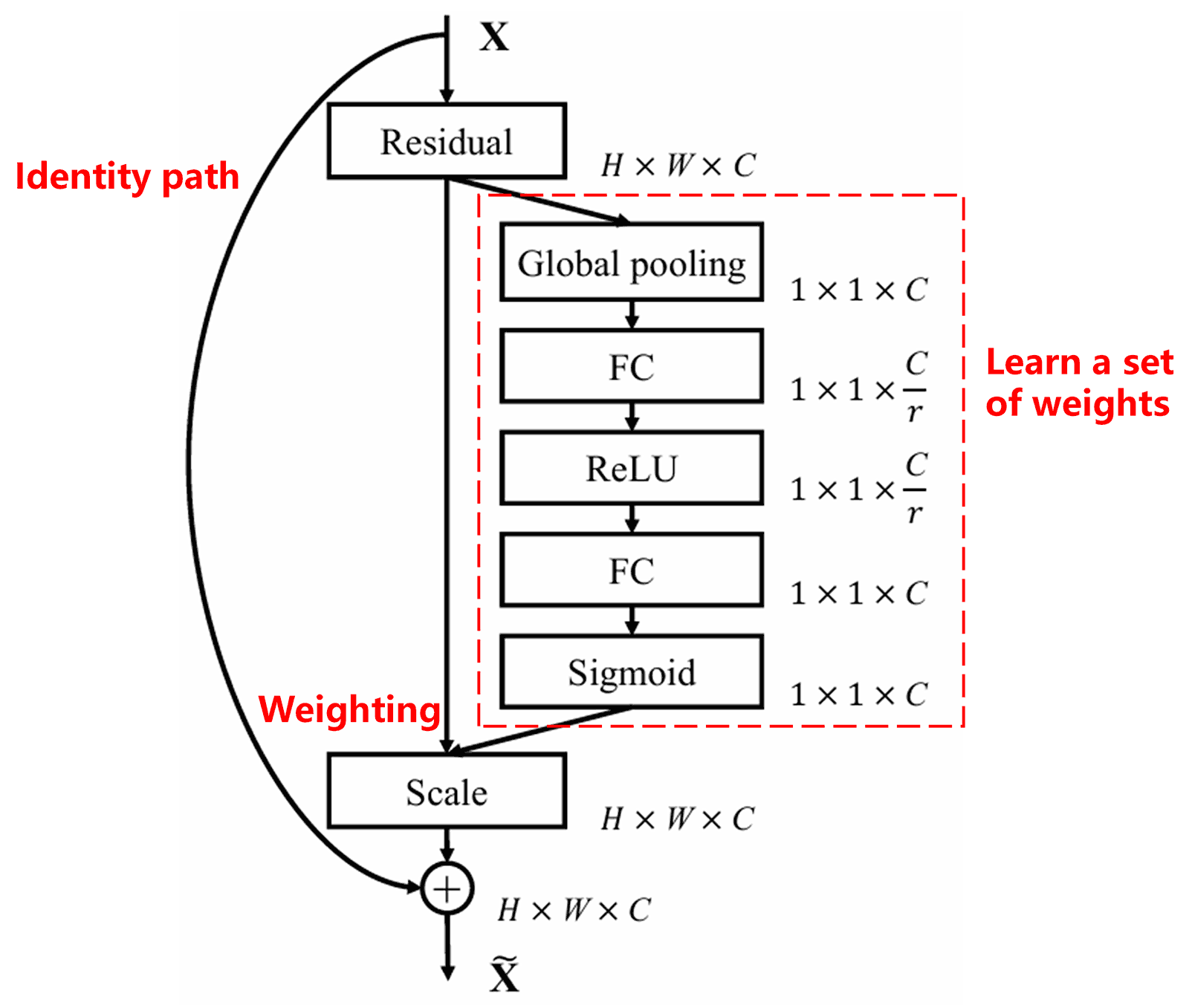
4. Soft Thresholding with Deep Attention Mechanism
Deep Residual Shrinkage Network اوپر بیان کیے گئے SENet sub-network structure سے inspiration لیتا ہے تاکہ deep attention mechanism کے تحت soft thresholding کو implement کیا جا سکے۔ Sub-network (جو سرخ باکس میں دکھایا گیا ہے) کے ذریعے، Learn a set of thresholds (thresholds کا ایک set learn کیا جا سکتا ہے) تاکہ ہر feature channel پر Soft thresholding apply کی جا سکے۔
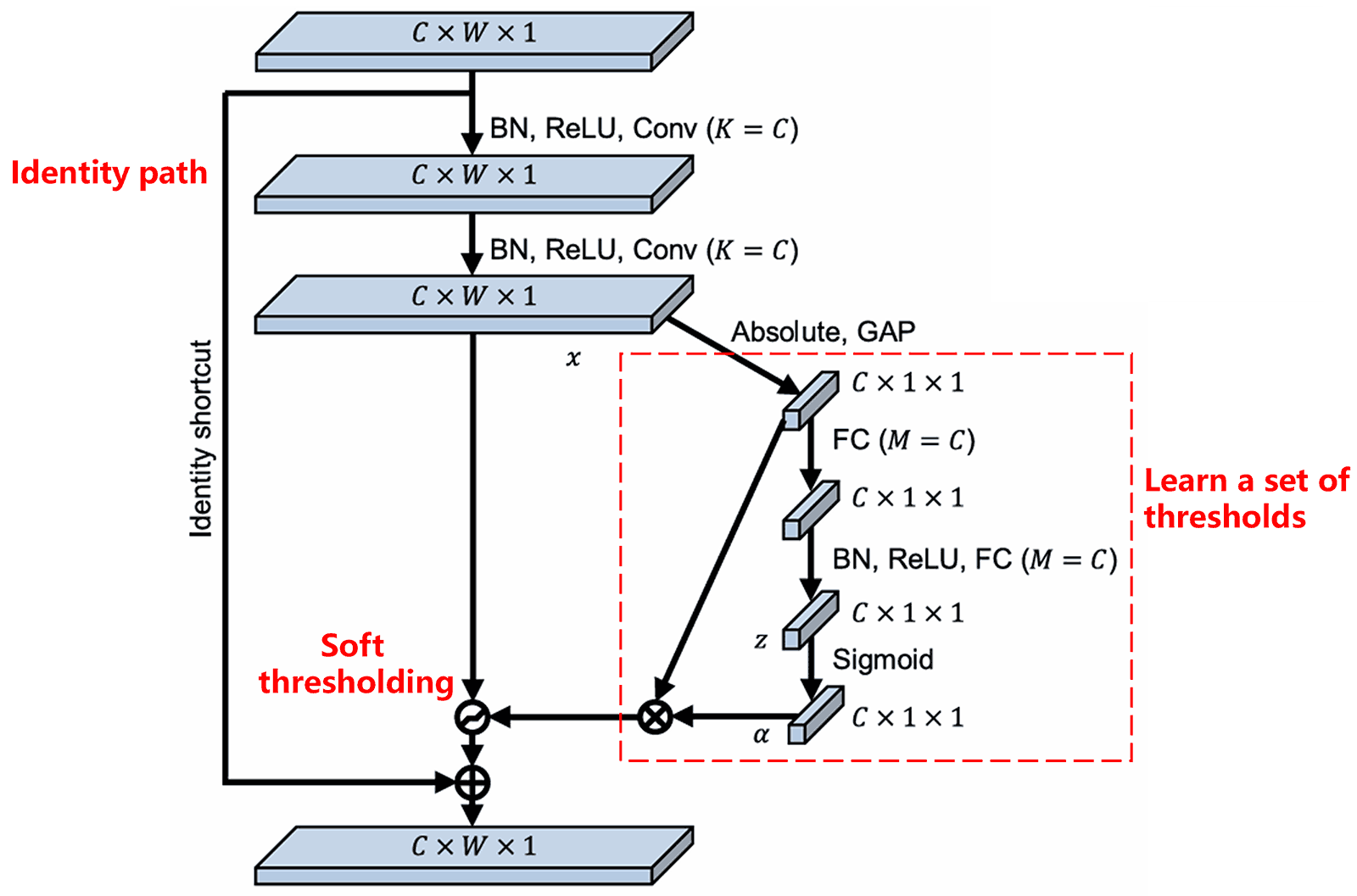
اس sub-network میں، پہلے input feature map کے تمام features کی absolute values calculate کی جاتی ہیں۔ پھر، global average pooling اور averaging کے ذریعے، ایک feature حاصل کیا جاتا ہے، جسے A کہا جاتا ہے۔ دوسری path میں، global average pooling کے بعد feature map کو ایک چھوٹے fully connected network میں input کیا جاتا ہے۔ یہ fully connected network، Sigmoid function کو اپنی final layer کے طور پر use کرتا ہے تاکہ output کو 0 اور 1 کے درمیان normalize کیا جا سکے، جس سے ایک coefficient حاصل ہوتا ہے جسے α کہا جاتا ہے۔ Final threshold کو α×A کے طور پر express کیا جا سکتا ہے۔ اس لیے، threshold 0 اور 1 کے درمیان ایک number اور feature map کی absolute values کی average کا product ہے۔ یہ method اس بات کو یقینی بناتا ہے کہ threshold نہ صرف positive ہو بلکہ بہت زیادہ بڑا بھی نہ ہو۔
مزید برآں، different samples کے نتیجے میں different thresholds آتے ہیں۔ نتیجتاً، ایک حد تک، اسے ایک specialized attention mechanism سمجھا جا سکتا ہے: یہ current task سے irrelevant features کو identify کرتا ہے، انہیں دو convolutional layers کے ذریعے zero کے قریب values میں transform کرتا ہے، اور soft thresholding use کر کے انہیں zero سیٹ کر دیتا ہے؛ یا پھر، یہ current task سے relevant features کو identify کرتا ہے، انہیں دو convolutional layers کے ذریعے zero سے دور values میں transform کرتا ہے، اور انہیں preserve کرتا ہے۔
آخر میں، Stack many basic modules (basic modules کی ایک خاص تعداد کو stack کر کے) ساتھ ہی convolutional layers، batch normalization، activation functions، global average pooling، اور fully connected output layers کے ساتھ، مکمل Deep Residual Shrinkage Network construct کیا جاتا ہے۔ Diagram میں Identity path، information flow کو آسان بناتا ہے۔
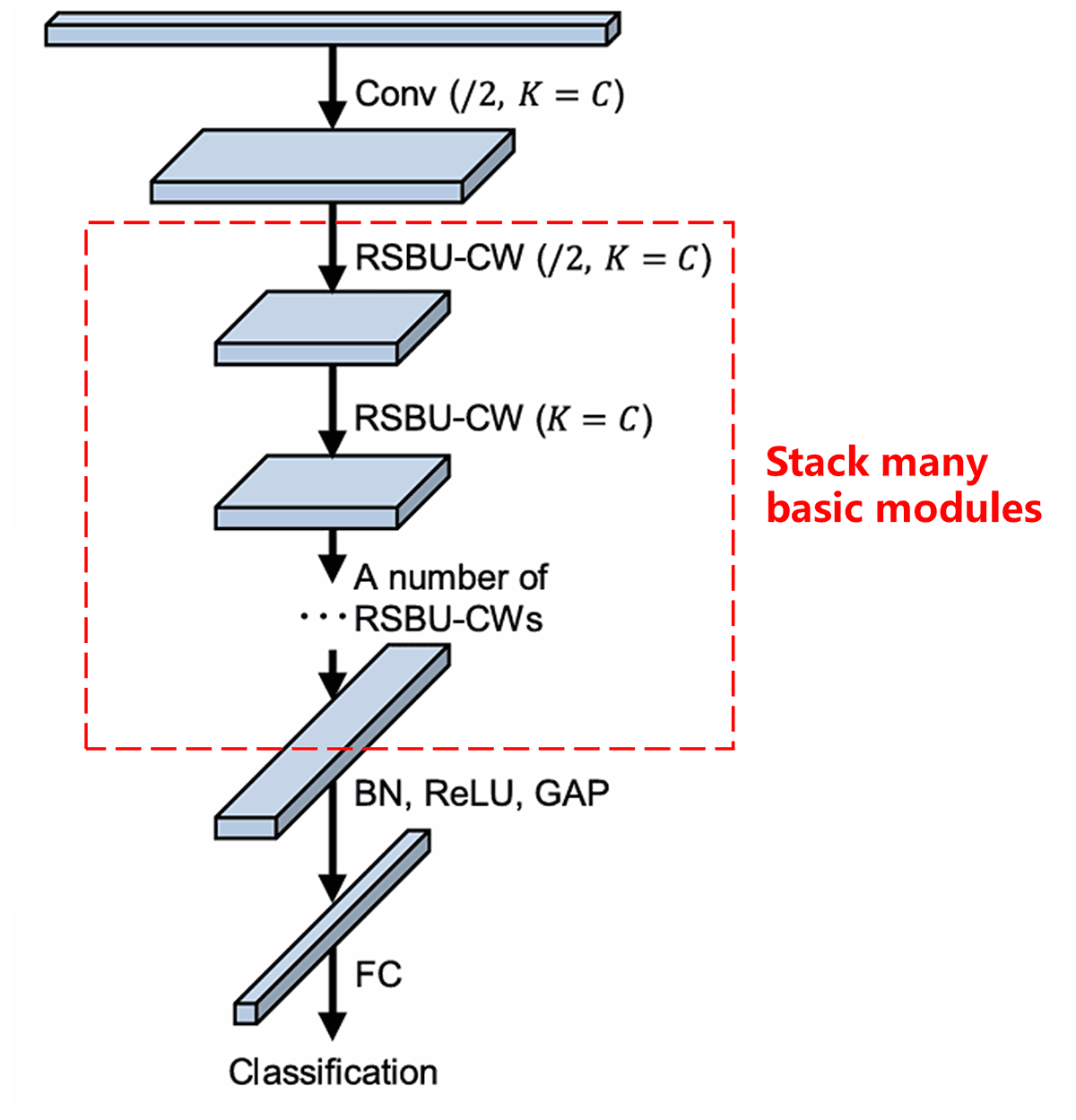
5. Generalization Capability
Deep Residual Shrinkage Network درحقیقت ایک general feature learning method ہے۔ اس کی وجہ یہ ہے کہ بہت سے feature learning tasks میں، samples میں کم و بیش کچھ noise اور irrelevant information شامل ہوتی ہے۔ یہ noise اور irrelevant information، feature learning کی performance کو متاثر کر سکتی ہے۔ مثال کے طور پر:
Image classification میں، اگر ایک image میں ایک ہی وقت میں بہت سے دوسرے objects ہوں، تو ان objects کو “noise” سمجھا جا سکتا ہے۔ Deep Residual Shrinkage Network شاید attention mechanism کو use کر کے اس “noise” کو notice کر سکے اور پھر soft thresholding کے ذریعے اس “noise” کے corresponding features کو zero سیٹ کر دے، جس سے image classification accuracy improve ہو سکتی ہے۔
Speech recognition میں، خاص طور پر relatively noisy environments میں جیسے کہ سڑک کے کنارے بات چیت یا factory workshop کے اندر، Deep Residual Shrinkage Network، speech recognition accuracy کو improve کر سکتا ہے، یا کم از کم، ایک ایسا methodology provide کرتا ہے جو speech recognition accuracy کو improve کرنے کی صلاحیت رکھتا ہے۔
6. Academic Impact
اس paper کو Google Scholar پر 1,400 سے زیادہ citations مل چکی ہیں۔
نامکمل statistics کی بنیاد پر، Deep Residual Shrinkage Network (DRSN) کو mechanical engineering، electrical power، vision، healthcare، speech، text، radar، اور remote sensing سمیت وسیع fields میں 1,000 سے زیادہ publications/studies میں براہ راست apply کیا گیا ہے یا modify کر کے apply کیا گیا ہے۔
حوالہ جات (Reference)
BibTeX
@article{Zhao2020,
author = {Minghang Zhao and Shisheng Zhong and Xuyun Fu and Baoping Tang and Michael Pecht},
title = {Deep Residual Shrinkage Networks for Fault Diagnosis},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics},
year = {2020},
volume = {16},
number = {7},
pages = {4681-4690},
doi = {10.1109/TII.2019.2943898}
}